Unterschiede zwischen 850 nm, 940nm, und 1064nm nahe Infrarotlicht
In der modernen medizinischen Ästhetik, Nahinfrarot (Nir) Licht ist zu einem leistungsstarken Werkzeug zur Hautaufhellung geworden, Fleckenreduzierung, Verjüngung, und Reparatur dank seiner nicht-invasiven Natur, tiefes Eindringen, und schnelle Genesung. Zu den am häufigsten verwendeten Wellenlängen –850nm, 940nm, und 1064 nm–jedes verfügt über einzigartige Wirkmechanismen und klinischen Wert.
Viele Leute fragen sich: Was genau sind die Unterschiede zwischen diesen drei Wellenlängen?? Für welche Hautprobleme sind sie am besten geeignet?? Müssen sie in Kombination verwendet werden?? Dieser Artikel gibt Ihnen einen klaren Überblick.
850nm Nahinfrarotlicht: Kollagenreparatur & Verbesserung der Hautqualität
Schlüsselmerkmale
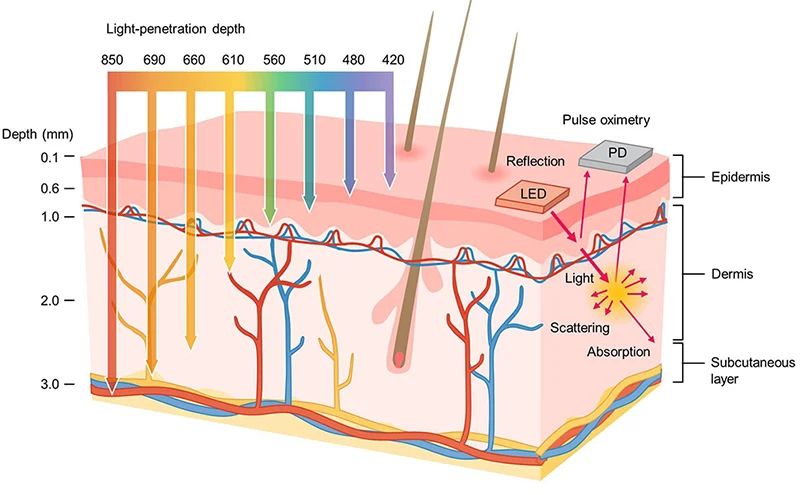
Eindringtiefe: ~2–3 mm
Aktiviert Fibroblasten, stimuliert die Kollagen- und Elastinproduktion
Verbessert die Elastizität und Ausstrahlung der Haut
Entzündungshemmende und reparierende Wirkung, Reduzierung der postinflammatorischen Hyperpigmentierung
Beste Anwendungen
Behandlung oberflächlicher Pigmentierung
Bleaching und punktuelle Aufhellung als Zusatztherapie
Anti-Aging und Verbesserung der Hautstruktur
Zusamenfassend, 850nm ist der „Kollagen-Reparatur-Experte“, Ideal zur Verbesserung der Hautqualität und zur Kontrolle der oberflächlichen Pigmentierung.
940nm Nahinfrarotlicht: Gefäß & Stoffwechselregulation
Schlüsselmerkmale
Eindringtiefe: ~3–4 mm
Leicht vom Hämoglobin absorbiert, Hilft, abnormale Kapillaren abzudichten
Reduziert Rötungen und Entzündungsreaktionen
Verbessert die Lymphzirkulation, Beschleunigung der Beseitigung von Melanin und Stoffwechselabfällen
Beste Anwendungen
Rötung, Teleangiektasie, Rosacea
Entzündliche Pigmentierung
Unterstützende Behandlung von Melasma
940nm ist als bekannt „Hautstoffwechselregulator“, Besonders wirksam bei Haut mit Gefäßproblemen oder Rötungen.
1064nm Nahinfrarotlicht: Präzises Tiefenpigmentmanagement
Schlüsselmerkmale
Tiefste Penetration, die Dermis oder sogar das Unterhautgewebe erreichen
Starke Absorption durch Melaninkörnchen, Zersetzt tiefliegende Pigmente effektiv
Im gütegeschalteten Modus: Ota-Nävus behandeln, tiefe Sonnenflecken, und hartnäckige Pigmentierung
Im Niedrigenergiemodus: hemmt die Tyrosinaseaktivität, Reduzierung der Neubildung von Pigmenten
Sicherer für dunklere Hauttöne
Beste Anwendungen
Tiefe Pigmentierung (Z.B., Ota-Nävus, tiefe Sonnenflecken)
Langfristiges Melasma-Management
Sicheres Aufhellen für verschiedene Hauttypen
1064nm ist der „Radiergummi für tiefe Pigmente“, unverzichtbar bei der Behandlung hartnäckiger Pigmentierung.
Kernunterschiede zwischen den drei Wellenlängen
Eindringtiefe: 850nm (oberflächlich) < 940nm (mittlere Dermis) < 1064nm (tiefe Dermis)
Primäre Ziele:
850nm → Kollagen & Mikrozirkulation
940nm → Blutgefäße & Lymphgefäße
1064nm → Melaninkörnchen
Anwendungsfokus:
850nm → Aufhellung, Verjüngung, Hautstruktur
940nm → Gefäßprobleme, entzündliche Pigmentierung
1064nm → tiefe Pigmentierung, Melasma-Management
Wert der kombinierten Nutzung
In der klinischen Praxis, Eine einzige Wellenlänge kann oft nicht alle Probleme lösen. Multi-Wellenlängen-Kombinationen liegen mittlerweile im Trend.
Mehrschichtiges Targeting: 850nm verbessert die epidermale Mikroumgebung, 940nm stabilisiert Blutgefäße, und 1064 nm eliminiert tiefe Pigmente.
Stoffwechselsynergie: 1064nm klärt Pigmente → 850 nm und 940 nm beschleunigen die Lymphdrainage und den Stoffwechsel.
Reparieren & Wartung: 850nm fördert die Kollagenregeneration, während 940 nm Entzündungen unterdrückt, Verringerung des Risikos eines erneuten Auftretens.
Gesamtvorteile: umfassendere Ergebnisse, weniger Nebenwirkungen, und breitere Hauteignung.




