Differences Between 850nm, 940nm, and 1064nm Near-Infrared Light
In modern medical aesthetics, near-infrared (NIR) light has become a powerful tool for skin whitening, spot reduction, rejuvenation, and repair thanks to its non-invasive nature, deep penetration, and quick recovery. Among the most commonly used wavelengths—850nm, 940nm, and 1064nm—each has unique mechanisms of action and clinical value.
Many people wonder: what exactly are the differences between these three wavelengths? Which skin concerns are they best suited for? Do they need to be used in combination? This article will give you a clear overview.
850nm Near-Infrared Light: Collagen Repair & Skin Quality Enhancement
Key Features
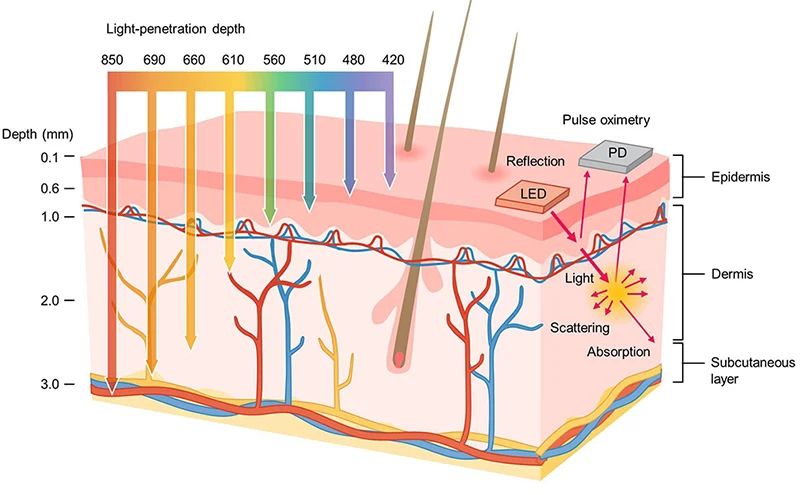
Penetration depth: ~2–3 mm
Activates fibroblasts, stimulates collagen and elastin production
Improves skin elasticity and radiance
Anti-inflammatory and reparative effects, reducing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Best Applications
Management of superficial pigmentation
Whitening and spot-lightening as adjunctive therapy
Anti-aging and skin texture improvement
In short, 850nm is the “collagen repair expert”, ideal for skin quality enhancement and superficial pigmentation control.
940nm Near-Infrared Light: Vascular & Metabolic Regulation
Key Features
Penetration depth: ~3–4 mm
Easily absorbed by hemoglobin, helps seal abnormal capillaries
Reduces redness and inflammatory responses
Enhances lymphatic circulation, accelerating the clearance of melanin and metabolic waste
Best Applications
Redness, telangiectasia, rosacea
Inflammatory pigmentation
Supportive treatment for melasma
940nm is known as the “skin metabolism regulator”, especially effective for skin with vascular issues or redness.
1064nm Near-Infrared Light: Precise Deep Pigment Management
Key Features
Deepest penetration, reaching the dermis or even subcutaneous tissue
Strong absorption by melanin granules, effectively breaks down deep pigment
In Q-switched mode: treats Ota nevus, deep sunspots, and stubborn pigmentation
In low-energy mode: inhibits tyrosinase activity, reducing new pigment formation
Safer for darker skin tones
Best Applications
Deep pigmentation (e.g., Ota nevus, deep sunspots)
Long-term melasma management
Safe whitening across diverse skin types
1064nm is the “deep pigment eraser”, indispensable in managing stubborn pigmentation.
Core Differences Between the Three Wavelengths
Penetration depth: 850nm (superficial) < 940nm (mid-dermis) < 1064nm (deep dermis)
Primary targets:
850nm → collagen & microcirculation
940nm → blood vessels & lymphatics
1064nm → melanin granules
Application focus:
850nm → whitening, rejuvenation, skin texture
940nm → vascular concerns, inflammatory pigmentation
1064nm → deep pigmentation, melasma management
Value of Combined Use
In clinical practice, a single wavelength often cannot solve all issues. Multi-wavelength combinations are now the trend.
Layered targeting: 850nm improves the epidermal microenvironment, 940nm stabilizes blood vessels, and 1064nm eliminates deep pigment.
Metabolic synergy: 1064nm clears pigment → 850nm and 940nm accelerate lymphatic drainage and metabolism.
Repair & maintenance: 850nm promotes collagen regeneration, while 940nm suppresses inflammation, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Overall benefits: more comprehensive results, fewer side effects, and broader skin suitability.




